Set-level inference (Gaussian)¶
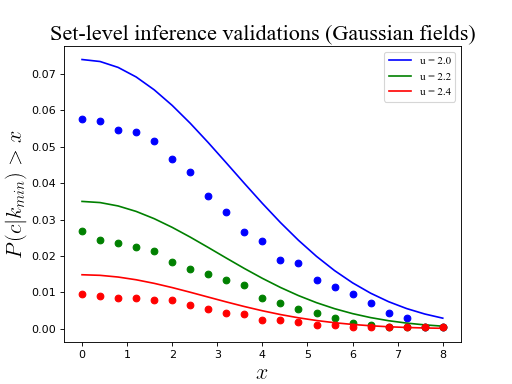
Set-level inference refers to the probability that 1D Gaussian fields will produce at least c upcrossings with a minimum extent of k when thresholded at a value u. This probability pertains to the entire excursion set (i.e. all field regions which exceed u). The basic procedure for RFT validations is outlined in Examples/Basic/Validating. Only code details are provided below.
See also ./rft1d/examples/val_upx_0_gauss_set.py
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot
import rft1d
eps = np.finfo(float).eps #smallest float
#(0) Test on one random field:
np.random.seed(0)
nResponses = 2000
nNodes = 101
FWHM = 8.5
interp = True
wrap = True
heights = [2.0, 2.2, 2.4]
c = 2
### generate data:
y = rft1d.randn1d(nResponses, nNodes, FWHM)
calc = rft1d.geom.ClusterMetricCalculator()
rftcalc = rft1d.prob.RFTCalculator(STAT='Z', nodes=nNodes, FWHM=FWHM)
#(1) Maximum region size:
K0 = np.linspace(eps, 8, 21)
K = [[calc.cluster_extents(yy, h, interp, wrap) for yy in y] for h in heights]
### compute number of upcrossings above a threshold:
C = np.array([[[ sum([kkk>=k0 for kkk in kk]) for kk in k] for k in K] for k0 in K0])
P = np.mean(C>=c, axis=2).T
P0 = np.array([[rftcalc.p.set(c, k0, h) for h in heights] for k0 in K0/FWHM]).T
#(2) Plot results:
pyplot.close('all')
colors = ['b', 'g', 'r']
ax = pyplot.axes()
for color,p,p0,u in zip(colors,P,P0,heights):
ax.plot(K0, p, 'o', color=color)
ax.plot(K0, p0, '-', color=color, label='u = %.1f'%u)
ax.set_xlabel('$x$', size=20)
ax.set_ylabel('$P(c | k_min) > x$', size=20)
ax.legend()
ax.set_title('Set-level inference validations (Gaussian fields)', size=20)
pyplot.show()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
Warning
As reported in Friston et al. (1994), RFT tends to predict slightly higher p values than are obtained in simulation. This is not considered a serious limitation because (a) critical RFT thresholds are accurate, and (b) RFT set-level probability values err in the conservative direction.